| |
Whats' New in Gauss 15
New Tools for Graphics
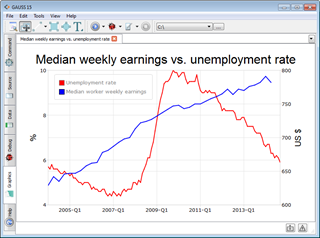 New
tools facilitate efficient and more versatile annotation and
customization of graphs making production and replication of
publication graphics easy. Add point labels, customize text boxes,
control export settings, and save project-specific graph default
preferences. New
tools facilitate efficient and more versatile annotation and
customization of graphs making production and replication of
publication graphics easy. Add point labels, customize text boxes,
control export settings, and save project-specific graph default
preferences.
- Live preview of exported graph
- Easy graph resizing
- Copy and paste graphs to Powerpoint® and Word®
- Program format of added text boxes, shapes, and arrows
- Easy, (x,y) coordinate placement of annotations
- Control of annotation background color and opacity, line thickness, and font appearance
- Improved Formatting Versatility
- Opacity control for bar,box, and area fills
- Add string labels to bar and boxplot graphs
- Easy formatting of tic labels
- Multiple y-axes
- Create and format area plots
- Add area graphs to existing graphs
- Control area opacity, fill, and style
New Parallel for Loops
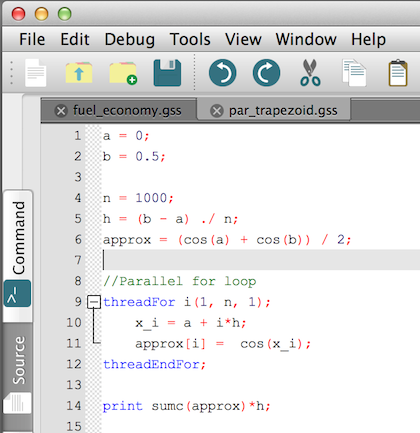 Single command parallel for looping yields increased looping speed. See a parallel rolling regression example: Single command parallel for looping yields increased looping speed. See a parallel rolling regression example:
The new parallel for loops provided by the new GAUSS keyword threadFor,
in version 15 give you a compact method to add threading to your GAUSS
program.
Rolling Regression Example
Rolling regression is a natural candidate for parallelization. First,
we load some data and prepare our variables for the rolling regression:
//Load AR(1) data
filename = "ar1data.xlsx";
range = "a2:b501";
sheet = 1;
data = SpreadsheetReadM(filename,range,sheet);
//Create x and y variable
x = packr(lag1(data[.,2]));
y = data[2:rows(data),2];
//Window for rolling regression
window = 50;
Now we are ready to perform the regression. Here is an implementation using a standard for loop:
//Pre-initialize vector to hold estimates
b = zeros(rows(x)-window,1);
//Estimate each window
for i(1,rows(x)-window,1);
b[i] = y[i:i+window]/x[i:i+window];
endfor;
//Combine and print out our results
print "average beta"; meanc(b);
Adding parallelization
The threads created by
threadFor all share the same memory, so each thread can access any of
the GAUSS global variables. There is no problem reading from the same
global variable in multiple threads. With the threadFor loop in GAUSS
you can even assign to the same global variable from multiple threads
as long as you are not assigning to the same elements from more than
one thread. Therefore, all we can parallelize the above loop, by simply
change the for to threadFor and the endfor to threadEndFor like this:
//Pre-initialize vector to hold estimates
b = zeros(rows(x)-window,1);
//Estimate each window in parallel
threadFor i(1,rows(x)-window,1);
b[i] = y[i:i+window]/x[i:i+window];
threadEndFor;
//Combine and print out our results
print "average beta"; meanc(b);
Enriched Project Management
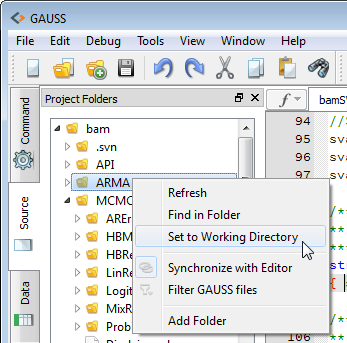 Enhanced
interaction with system files allows you to rename and delete files
from the file system, filter the file list, and perform quick searches
for files in source paths and project folders. Enhanced
interaction with system files allows you to rename and delete files
from the file system, filter the file list, and perform quick searches
for files in source paths and project folders.
- Easily search throughout a selected folder or set your working directory
- Quickly locate any file in your project folders or GAUSS source path
- Rename and delete files directly from GAUSS
Improved Source Browsing
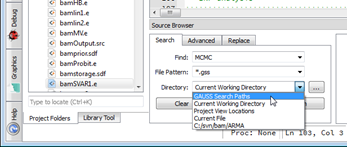 Prepopulated directory options make the Source Browser more intuitive and easier to use. Prepopulated directory options make the Source Browser more intuitive and easier to use.
Improved Data Editor
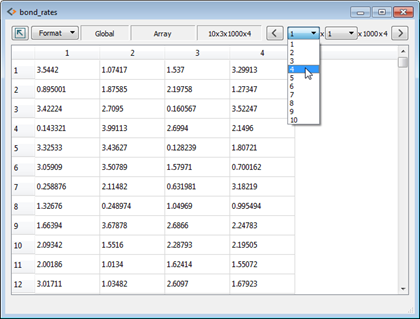 New
data editor structure makes viewing, editing, and interacting with data
easier while using less memory. Work seamlessly and efficiently with
large multidimensional data. New
data editor structure makes viewing, editing, and interacting with data
easier while using less memory. Work seamlessly and efficiently with
large multidimensional data.
- Improved navigation of multidimensional arrays
- Drop down menu to select dimensions
- Right and left arrow button to traverse array dimensions
Support for Retina Display on Mac
View GAUSS and the improved graphics in stunning HiDPI.
Random Number and Matrix Decomposition Functionality (New)
- LDL factorization and solver for LDL factorized matrix
- Sobol and Niederreiter random number generators
- Chi-squared and non-central chi-squared random number generators
© Copyright 2015 Aptech
Systems, Inc.


|
p
|