GOALS
This tutorial will explain the options available in the gmmControl structure and their usage. After this tutorial, you should be able to:
- Declare an instance of the
gmmControlstructure - Specify the GMM modeling method
- Control the initial weighting matrix
- Set the weight matrix method
THE GMMCONTROL STRUCTURE
GAUSS GMM estimation implements pre-determined default modeling parameters to allow you to estimate models with minimal programming. However, you are also able to set custom modeling options using the gmmControl structure. Using the gmmControl structure requires three steps:
- Declare an instance of the
gmmControlstructure.
//Declare 'gctl' to be a 'gmmControl' structure struct gmmControl gctl;
- Fill the created structure with default parameter values using
gmmControlCreate.
//Fill 'gctl' with default settings gctl = gmmControlCreate();
- Change the desired modeling parameters using the appropriate
gmmControlmembers.
gctl.method = "iterative";
MODELING METHOD:GCTL.METHOD
One of the options that can be controlled with the gmmControl structure is which computation method is used. This is done using the gmmControl structure member gctl.method. There are four modeling options, each discussed in more detail below, that you may use:
- One-step GMM
- Two-step GMM
- Iterative GMM
- Continuously updating GMM.
ONE-STEP GMM
One-step GMM estimation is the simplest estimation technique. It uses the initial weighting matrix in the GMM objective function and estimation is achieved in “one-step” without updating the weighting matrix.
To specify one-step GMM estimation in GAUSS the member method in the gmmControl structure should be set equal to “onestep”.
//Specify one-step estimation gctl.method = "onestep";
TWO-STEP GMM (DEFAULT METHOD)
Like one-step estimation, two-step GMM starts with the initial weighting matrix in the GMM objective function. The weight matrix is then updated using the first-step parameter estimates are obtained. Final estimates are found using the updated weight matrix and the parameter estimates from the first step in the objective function.
To specify two-step GMM estimation in GAUSS the member method in the gmmControl structure should be set equal to “twostep”:
//Specify two-step estimation gctl.method = "twostep";
ITERATIVE GMM
Iterative estimation follows the same steps outlined above for two-step GMM estimation:
- Pick the initial weight matrix.
- Estimate the parameters using the weight initial matrix.
- Update the weight matrix using the estimated parameters.
- Update parameter estimates using new weight matrix.
However, iterative GMM repeats steps 2-4 until a specified level of convergence is achieved. To specify iterative GMM estimation in GAUSS the member method in the gmmControl structure should be set equal to “iter”:
//Specify iterative GMM estimation gctl.method = "iter";
The iterative estimation process is completed when the change in either the weight matrix or the parameter estimates is less than the specified tolerance levels or the maximum number of iterations is reached.
© 2025 Aptech Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
By default, both the weight matrix and parameter tolerances are 1e-5. The default maximum number of iterations is set to 500. These defaults can be changed using the gmmControl struct members gctl.gIter.paramTol, gctl.gIter.wTol, and gctl.gIter.maxIters. For example, consider changing the maximum number of iterations from 500 to 1000:
//Set maximum number of iterations for //iterative GMM to 1000 gctl.gIter.maxIters = 1000;
CONTINUOUS UPDATING GMM
Continuous updating GMM simultaneously estimates both the weight matrix and parameters using the GMM objective function:
![]()
To specify continuously updating GMM estimation in GAUSS the member method in the gmmControl structure should be set equal to “cu”:
//Specify continuous updating GMM gctl.method = "cu";
INITIAL WEIGHT MATRIX: gctl.wInit and gctl.wInitMat
Two members of the gmmControl structure are used to control the initial weight matrix used in the GMM estimation, gctl.wInit and gmm.wInitMat. The member gctl.wInit is a string indicator used to set an internally computed initial weight matrix type.
//Set initial weight matrix gctl.wInitMat = invpd( (1/rows(X)) * (X'X) );
THE gmmFit PROCEDURE
- The default weight matrix for the
gmmFitprocedure is a K x K identity matrix where K is equal to the number of moments. - The only alternative to using the identity matrix is to specify an alternative initial weight matrix using the
gmmControlstructure membergctl.wInitMat. The specified matrix must be positive definite. For example, consider using an initial weight matrix equal to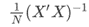 in the
in the gmmFitprocedure.
THE gmmFitIV PROCEDURE
- The default weight matrix for the
gmmFitIVprocedure is based on the matrix of exogenous variables. Assuming the model’s exogenous variables are stored in the matrix, z,gmmFitIVuses an initial weight matrix equal to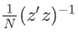
- The weight matrix can be changed to the identity matrix by setting the
gmmControlstructure membergctl.wInitequal to “identity”.
//Use identity matrix as initial weight matrix gctl.wInit = "identity";
GMM WEIGHT MATRIX: gctl.wType
The weight matrix used in the gmmFit and gmmFitIV procedures is controlled using the gctl.wType control structure member. The default GMM weight matrices for both GMM procedures assume serially uncorrelated sequences. However, in addition to the default weighting matrix, a heteroskedastic and autocorrelated robust weighting matrix may be implemented using the gmmControl structure member gctl.wType:
//HAC Weighting Matrix gctl.wType = "HAC";
The default HAC weighting kernel is the Bartlett kernel. However, the Parzen or Quadratic Spectral kernel may also be specified by changing the gmmControl structure member gctl.hacKernel
//Set HAC Kernel to Parzen gctl.hacKernel = "parzen";
CONCLUSION
Congratulations! You have:
- Declared an instance of the
gmmControlstructure. - Specified the GMM modeling method.
- Set the initial weighting matrix.
- Set the weight matrix method.
Now that we have been introduced to the GMM, the GAUSS GMM procedures and their control settings, our next tutorial will work through our first application, GMM for OLS with exogenous regressors.

