INTRODUCTION
This tutorial will explain the use of relational and logical operators in GAUSS.
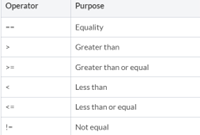
MATRIX RELATIONAL OPERATORS
- Return a scalar 1 if the statement is true for every element in the matrix, otherwise a 0.
SCALAR EQUALITY
a = 0.7; // Set 'c1' equal to 1 if // 'a' is greater than 0.5 c1 = a > 0.5; // Set 'c2' equal to 1 if // 'a' is less than 0.5 c2 = a < 0.5;
will assign
c1 = 1 c2 = 0
MATRIX INEQUALITY
In our first example, the variable a had only one element. Let’s look at a matrix example.
// Create a 2x3 matrix
a = { 0.1 0.5 0.4,
0.5 0.3 0.7 };
// Assign 'c1' to equal 1 if EVERY
// element of 'a' is > 0.4;
c1 = a > 0.4;
// Assign 'c2' to equal 1 if EVERY
// element of 'a' is < 0.8;
c2 = a < 0.8;
will assign
c1 = 0 c2 = 1
This time, c1 will be set equal to 0, because several of the elements of a are less than 0.4.
Whereas c2 will be set equal to 1, because every element of a is less than 0.8.
MATRIX EQUALITY
// Create a 2x3 matrix
a = { 0.1 0.5 0.4,
0.5 0.3 0.7 };
// Assign 'c1' to equal 1 if EVERY
// element of 'a' is equal 0.4;
c1 = a == 0.4;
// Assign 'c2' to equal 1 if EVERY
// element of 'a' does NOT equal 0.4
c2 = a != 0.4;
// Assign 'c3' to equal 1 if EVERY
// element of 'a' does NOT equal 0.8
c3 = a != 0.8;
After the code above:
c1 = 0 c2 = 0 c3 = 1
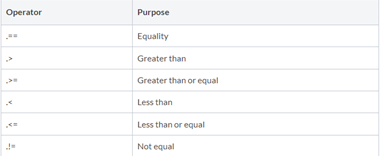
ELEMENT-BY-ELEMENT RELATIONAL OPERATORS
- Return a matrix or vector of 1’s and 0’s with a 1 at the location of the elements for which the operator returns true and a 0 for the other elements.
MATRIX ELEMENT‐BY‐ELEMENT INEQUALITY
The scalar case is the same as for the matrix operators, so we will start with a matrix example.
// Create a 2x3 matrix
a = { 0.1 0.5 0.4,
0.5 0.3 0.7 };
// Return a 2x3 matrix of 1's
// and 0's indicating whether the
// corresponding element of 'a'
// is > 0.4
c1 = a .> 0.4;
// Return a 2x3 matrix of 1's
// and 0's indicating whether the
// corresponding element of 'a'
// is ≤ 0.5
c2 = a .<= 0.5;
After the above code
c1 = 0 1 0
1 0 1
c2 = 1 1 1
1 1 0
ExE CONFORMABILITY
The ExE conformability of the GAUSS relational operators makes it simple make comparisons along rows or columns.
COLUMN INEQUALITY
// Create a 4x2 matrix
a = { 125 23,
150 31,
105 19,
150 33 };
// Create a 1x2 row vector
b = { 120 25 };
// Check which elements in the first column of 'a'
// are greater than the first element of 'b',
// and which elements of the second column of 'a'
// are greater than the second element of 'b'
c = a .> b;
The above code will assign:
c = 1 0
1 1
0 0
1 1
ROW INEQUALITY
// Create a 4x2 matrix
a = { 25 23,
50 31,
5 19,
41 33 };
// Create a 4x1 column vector
b = { 23,
31,
10,
50 };
// Check which elements in the rows of 'a'
// are less than or equal to the elements of the
// corresponding row of 'b'
c = a .<= b;
The above code will assign:
c = 0 1
0 1
1 0
1 1
SCALAR LOGICAL OPERATORS

SCALAR ‘AND’
a = 1; b = 9; x = 0; // Are both 'a' and 'b' non-zero? c1 = a and b; // Are both 'x' and 'a' non-zero? c2 = x and a; // Are both 'b' and 0 non-zero? c3 = b and 0;
will assign
c1 = 1 c2 = 0 c3 = 0
SCALAR ‘OR’
a = 1; b = 9; x = 0; // Is either 'a' or 'b', or both, non-zero? c1 = a or b; // Is either 'x' or 'a', or both, non-zero? c2 = x or a;
© 2025 Aptech Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
// Is either 'x' or 0, or both, non-zero? c3 = x or 0;
will assign
c1 = 1 c2 = 1 c3 = 0
SCALAR ‘NOT’
a = 1; b = 9; x = 0; // Is 'a' zero? c1 = not a; // Is 'x' zero? c2 = not x; // Does the expression (a and b) return zero? c3 = not (a and b);
will assign
c1 = 0 c2 = 1 c3 = 0
ELEMENT-BY-ELEMENT RELATIONAL OPERATORS

ELEMENT-BY-ELEMENT ‘.AND’
Matrix and scalar case.
a = { 1 2,
3 0 };
b = 9;
x = 0;
// Are both 'a' and 'b' non-zero?
c1 = a .and b;
// Are both 'a' and 'x' non-zero?
c2 = a .and x;
will assign
c1 = 1 1
1 0
c2 = 0 0
0 0
Matrix and matrix case.
a = { 1 2,
3 0 };
b = { 9 0,
1 1 };
// Are both 'a' and 'b' non-zero?
c1 = a .and b;
will assign
c1 = 1 0
1 0
Matrix and row vector case.
// 2x3 matrix
a = { 1 0 8,
0 3 1 };
// 1x3 row vector
b = { 9 0 1 };
// Are the corresponding elements of 'a' and 'b' non-zero?
c1 = a .and b;
will assign
c1 = 1 0 1
0 0 1
Matrix and column vector case.
// 3x3 matrix
a = { 1 0 8,
0 3 1,
1 1 0 };
// 3x1 column vector
b = { 2,
1,
0 };
// Are the corresponding elements of 'a' and 'b' non-zero?
c1 = a .and b;
will assign
c1 = 1 0 1
0 1 1
0 0 0
ELEMENT-BY-ELEMENT ‘.OR’
Matrix and scalar case.
a = { 1 2,
3 0 };
b = 9;
x = 0;
// Are the elements of either 'a' or 'b', or both, non-zero?
c1 = a .or b;
// Are the elements of either 'a' or 'x', or both, non-zero?
c2 = a .or x;
will assign
c1 = 1 1
1 1
c2 = 1 1
1 0
Matrix and matrix case.
a = { 1 2,
3 0 };
b = { 9 0,
1 1 };
// Are the elements of either 'a' or 'b', or both, non-zero?
c1 = a .or b;
will assign
c1 = 1 1
1 1
Matrix and row vector case.
// 2x3 matrix
a = { 1 0 8,
0 3 1 };
// 1x3 row vector
b = { 9 0 1 };
// Are the corresponding elements of either
// 'a' or 'b', or both, non-zero?
c1 = a .or b;
will assign
c1 = 1 0 1
1 1 1
Matrix and column vector case.
// 3x3 matrix
a = { 1 0 8,
0 3 1,
1 1 0 };
// 3x1 column vector
b = { 2,
1,
0 };
// Are the corresponding elements of either
// 'a' or 'b', or both, non-zero?
c1 = a .or b;
will assign
c1 = 1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 0
ELEMENT-BY-ELEMENT ‘.NOT’
a = { 4 6,
1 0,
8 2 };
// Are the elements of 'a' zero?
c1 = .not a;
will assign
c1 = 0 0
0 1
0 0

